Pinewoods Treefrog
Scientific name: Hyla femoralis
These very small frogs are sometimes called “Morse code frogs” because of their distinct call. Their coloring helps them blend into the trees and leaves they inhabit, but you can usually tell them apart from similar frogs because of the spots on the hidden sides of their back legs.
Appearance
Very small and slender, usually 1 to 1.5 inches long. Skin color varies from tans and browns to greens or grays, and they may have blotches or bands. Most have a distinct “bandit mask” band across their faces. They also have yellowish or orange spots on the backs of their legs.
Behavior
Pinewoods treefrogs are abundant in their natural habitat. These small native frogs prefer forests where they climb high into longleaf pines, and shelter in cabbage palms, bromeliads and pitcher plants. They lay eggs in shallow water like ditches or temporary pools, and they overwinter in old logs or under loose bark.
Sound
Pinewoods Treefrog
Pinewoods Treefrog Chorus
Food
Insectivores. They eat mainly flies, crickets, wasps and other small insects.
Habitat & Range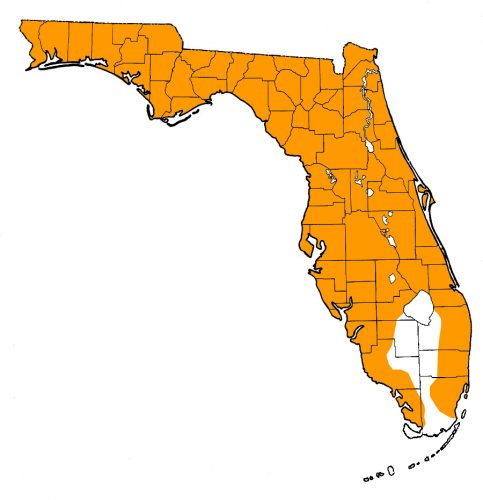
- Mainly the southeastern United States (west into Louisiana and north into Virginia)
- Florida: Statewide, except the Keys and central South Florida. Native.
- They prefer forests with small bodies of shallow water, and they are arboreal, which means they climb and live up in vegetation.
Notable
The tadpoles of these frogs usually have brightly colored tail fins, probably to distract predators away from their main body. Also, scientists and observers have noted these frogs fall silent during hurricane weather.
More info
3-D Print
- Have access to a 3-D printer? Download from MorphoSource


