Southern Leopard Frog
Scientific name: Lithobates sphenocephalus (or Rana sphenocephala)
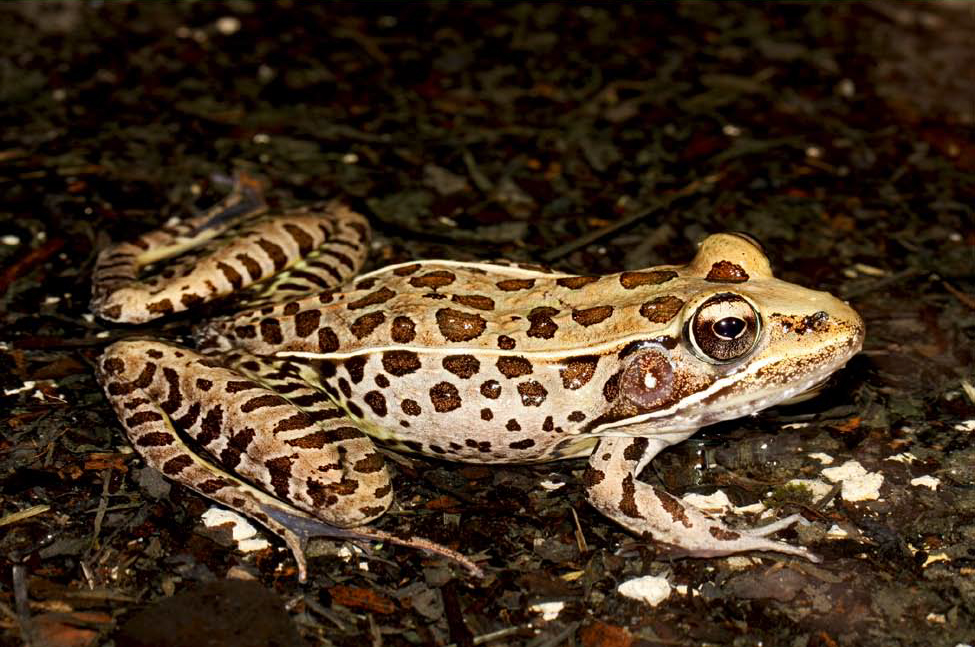
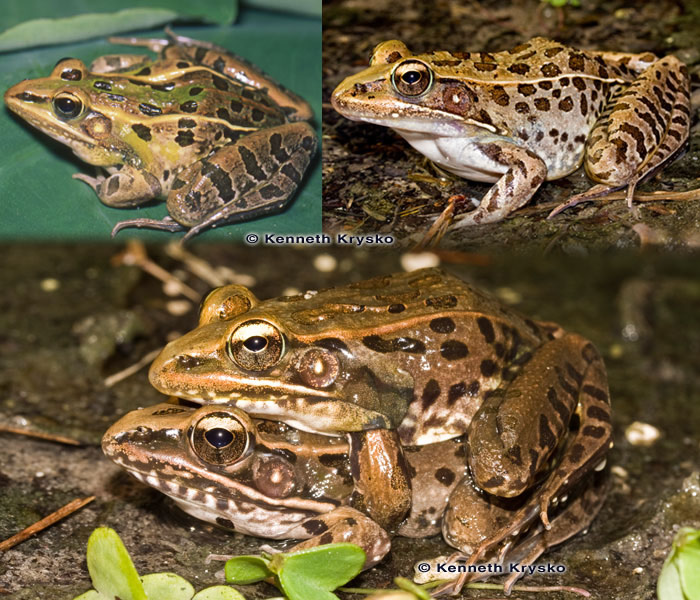
These are some of the most abundant frogs in Florida and are usually found in and around shallow bodies of water. They are true frogs and have a classic frog shape, and are marked with dark ‘leopard spots’ and a pair of light colored ridges down their backs.
Appearance
Large and athletic, usually 2 to 3.5 inches long, with webbed feet. Color is usually green to tan/brown, with irregular dark spots on back and legs that give them their ‘leopard’ name. They have a pair of light-colored ridges that run down their backs from eyes to groin. They have visible dark eardrums with a light spot in the center.
Behavior
Southern leopard frogs live around shallow freshwater bodies like bottomland swamps, floodplains and brackish ponds in hardwood forests. They’re urbanized and can live in man-made ponds, canals and ditches too. During the hotter months they often move up to dry land, but during the winter and breeding season they live in and around water for safety and to mate and lay eggs. Females can lay over 1,500 eggs at a time and the egg mass can be the size of a baseball.
Sound
Southern Leopard Frog
Food
They eat mainly insects, crayfish and small invertebrates.
 Habitat & Range
Habitat & Range
- Mainly the southeastern United States (west into Texas and north into Iowa and New York)
- Florida: Statewide except the northern Keys. Native.
- They are aquatic, which means they live in and around shallow bodies of water, but also climb onto land for long periods.
Notable
Southern leopard frogs are commonly hunted by humans for food and for use in the bait trade. They are prolific in their native ranges throughout the eastern United States, but there are introduced populations in the Bahamas and Southern California (although the California population has all but disappeared as far as researchers can tell).

