What’s going on?
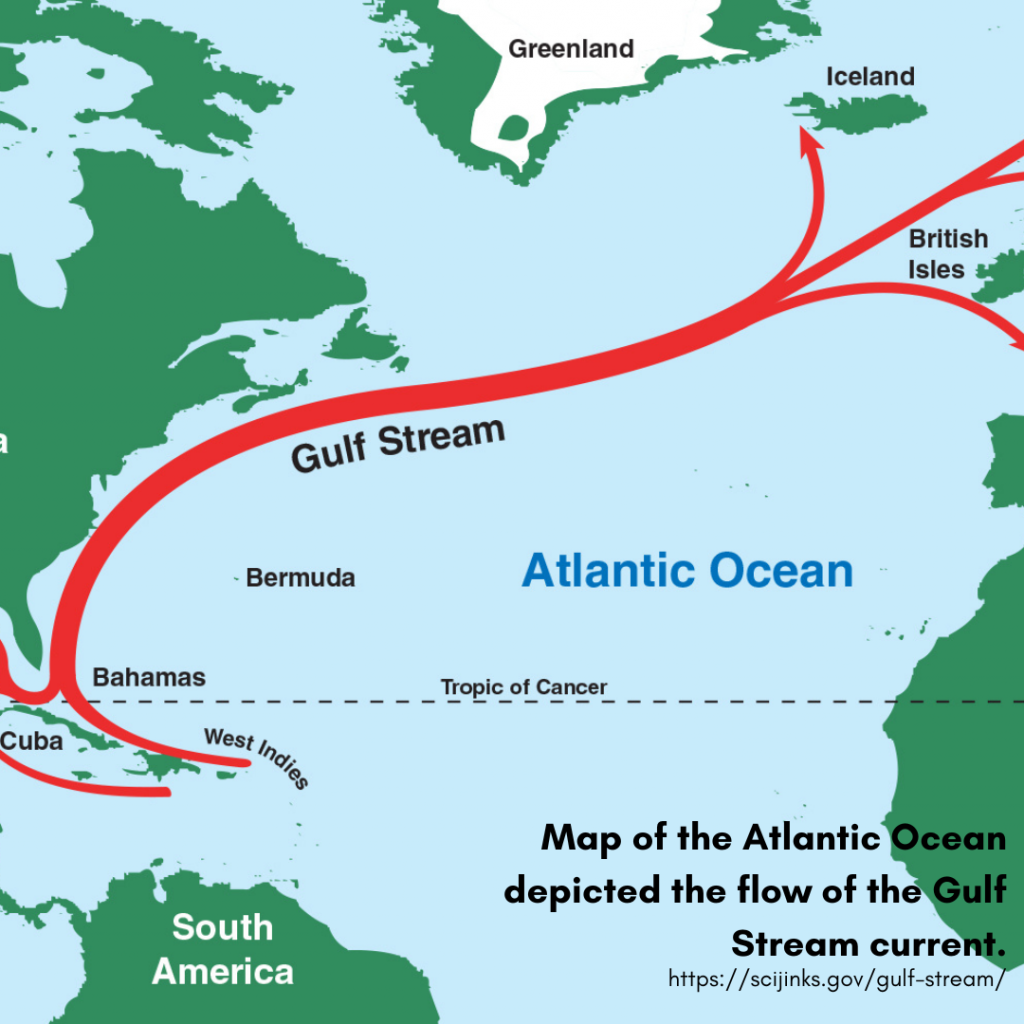
The Gulf Stream is a long ocean current that runs along the east coast of the United States and Canada, bringing the warm water from the Gulf of Mexico to the North Atlantic Ocean.
The water that the Gulf Stream deposits in the North Atlantic cools, sinks, and flows along the bottom of the ocean towards Antarctica. This process drives the flow of ocean water all over the planet.
 Recently, there has been a growing concern in the media surrounding the slowing or even collapse of the Gulf Stream. While a collapse is unlikely, there have been observed changes in the current. In 2023, the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution published a research paper that concluded the current has weakened. The study found that, over the last 40 years, the Gulf Stream has slowed by 4%.
Recently, there has been a growing concern in the media surrounding the slowing or even collapse of the Gulf Stream. While a collapse is unlikely, there have been observed changes in the current. In 2023, the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution published a research paper that concluded the current has weakened. The study found that, over the last 40 years, the Gulf Stream has slowed by 4%.
Why it matters.
The Gulf Stream is an extremely important current as it has an influence on the climate of the east coast of Florida. The current is also the reason that western European countries like England have a temperate climate.
Additionally, the Gulf Stream impacts the ecological processes of the ocean and plays a major role in the distribution of economically important fish species along the east coast of the U.S.
If the current were to continue to slow, the climates of the eastern U.S. and western Europe would change, as the warm water would not be flowing past these areas at the same pace.
Changes in the Gulf Stream may also affect hurricane activity and sea level rise in the Atlantic Ocean and disrupt the seasonal patterns of marine life.
What you can do.
Research is still being conducted to determine if the changes occurring in the Gulf Stream are from human-caused climate change or are a result of natural climate cycles. However, the current is still sensitive to climate change, and reducing carbon emissions is the best way to prevent these changes from worsening.
Information from NOAA, USGS, WHOI, and WBUR.