Trees in hardwood hammocks rarely grow to more than 50′ (15 m) due to inclement weather.


The tallest trees in hardwood hammocks, including the wild tamarind (Lysiloma latisiliqua) and gumbo limbo (Bursera simaruba), rarely grow more than 50 feet (15 m) in height due to cold weather, lightning, and strong winds. Mature hammocks form dense canopies, shading the internal environment from strong sunlight and maintaining a high level of humidity. Ferns and mosses thrive along the ground within this environment while bromeliads and orchids grow along the trunks and branches of the hammock trees.
The midstory of the hammock is occupied by smaller trees of the same species occurring in the canopy as well as some smaller tree species such as cinnamon bark (Canella winterana) and white stopper (Eugenia axillaris).


Beneath the midstory lies the understory which includes saplings of some canopy species as well as shrubs such as wild coffee (Psychotria undata) and white indigoberry (Randia aculeata). Other vegetation types include woody shrubs and vines with groundcover being very limited due to the lack of sunlight reaching the ground.
The outer edge of the hammock is densely wooded with vegetation requiring high levels of sunlight. This thick growth along the edges of the hammock maintains high humidity levels and cooler temperatures inside the hammock.
Species growing along the edges of hammocks include:



- Bahama strongbark (Bourreria radula), not shown
- saw palmetto (Serenoa repens)
- seven-year apple (Genipa clusiifolia), not shown
Native Fauna
- Wildlife living in hardwood hammocks originates from temperate regions in contrast to the native flora which originates from tropical regions

Wildlife residing in hardwood hammocks are mostly of temperate origin rather than tropical, in contrast to the characteristic plantlife. There has been no land connection with the West Indies, thereby limiting wildlife to those able to fly or to survive crossing the open seas.
Wildlife commonly sighted within hammocks include:
Invertebrates
- Florida tree snail (Liguus fasciatus)
Reptiles and Amphibians
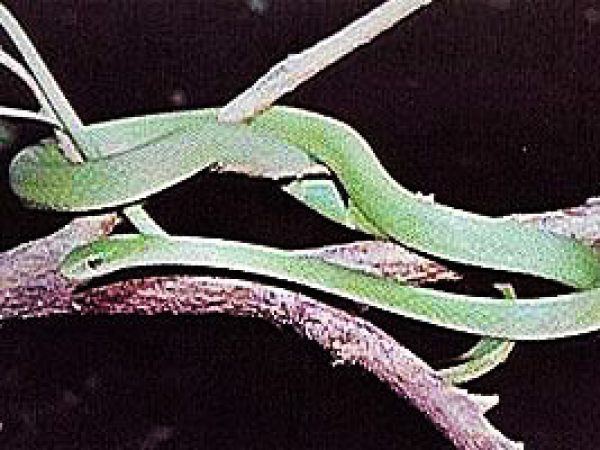
 Rough Green Snake (Opheodrys aestivus carinatus). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
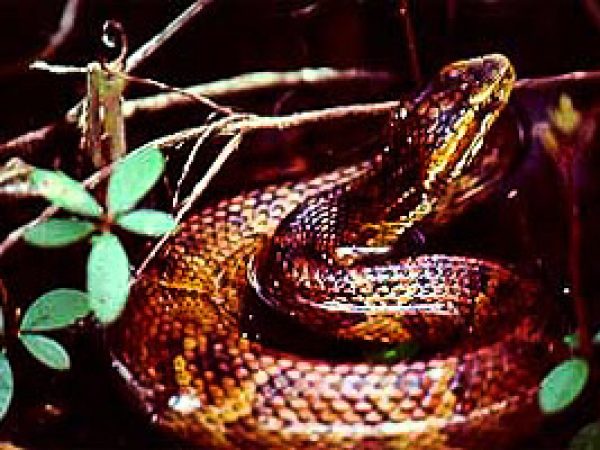
Rough Green Snake (Opheodrys aestivus carinatus). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Eastern Cottonmouth (Agkistrodon piscivorus). Photo courtesy U. S. Fish and Wildlife Service
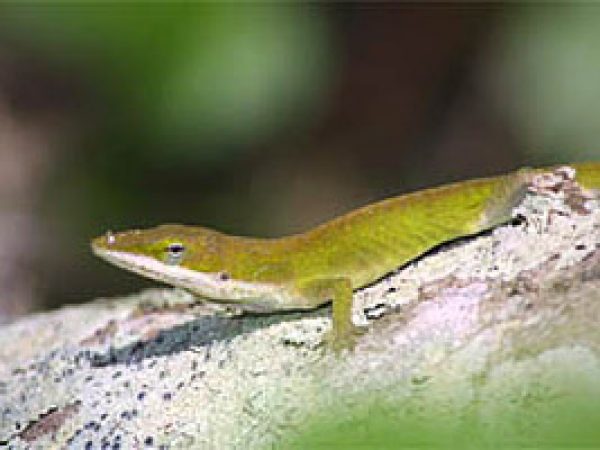
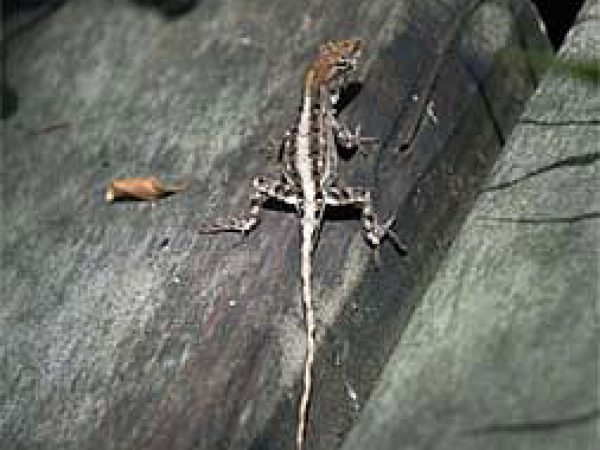
Eastern Cottonmouth (Agkistrodon piscivorus). Photo courtesy U. S. Fish and Wildlife Service Green Anole (Anolis carolinensis). Photo © Adam P. Summers, Museum of Vertebrate Zoology
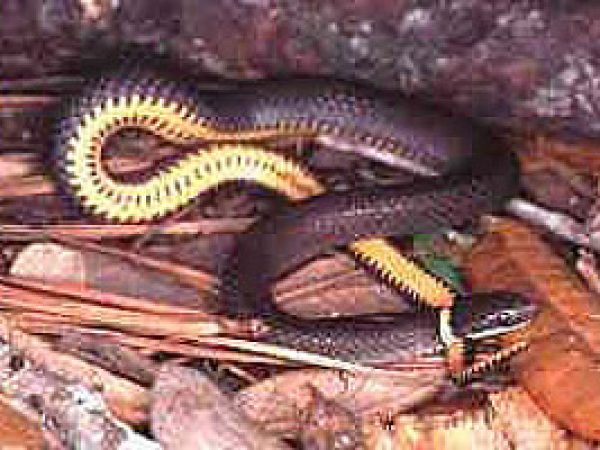
Green Anole (Anolis carolinensis). Photo © Adam P. Summers, Museum of Vertebrate Zoology Ringneck Snake (Diadophis punctatus). Photo © Kenneth Krysko
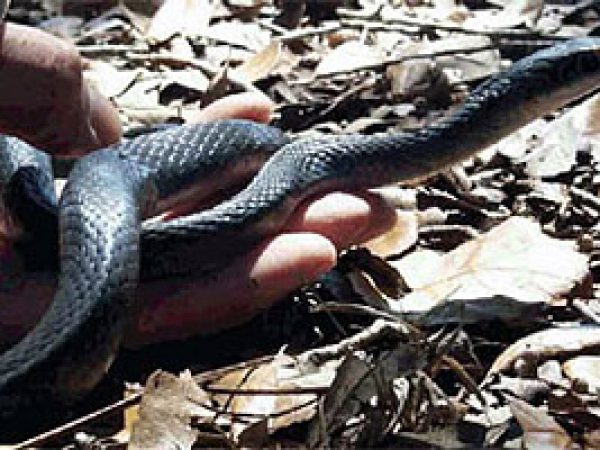
Ringneck Snake (Diadophis punctatus). Photo © Kenneth Krysko Everglades Racer (Coluber constrictor paludicola). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey
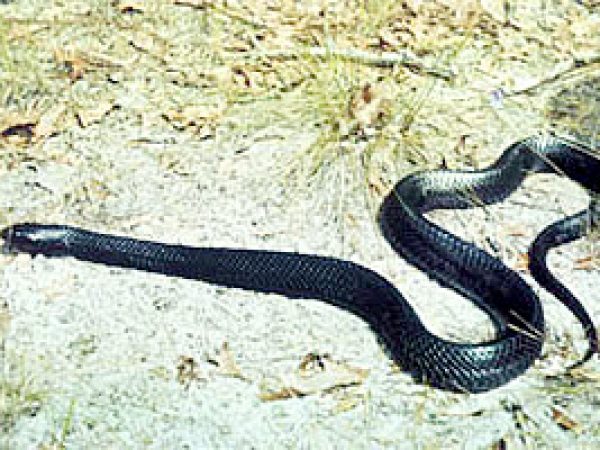
Everglades Racer (Coluber constrictor paludicola). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey Eastern Indigo Snake (Drymarchon coaris couperi). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
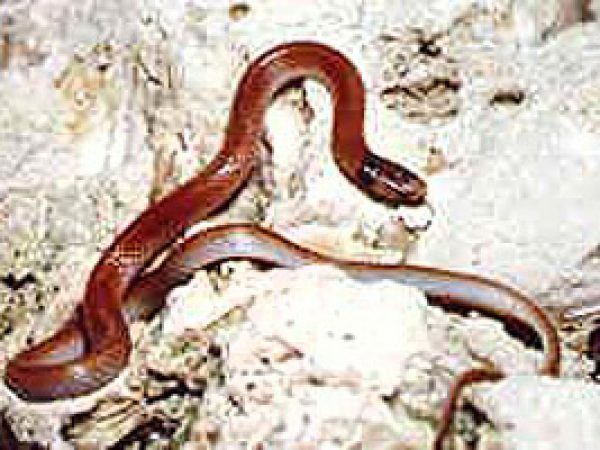
Eastern Indigo Snake (Drymarchon coaris couperi). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Rim Rock Crowned Snake (Tantilla oolitica). Photo © Kenneth Krysko
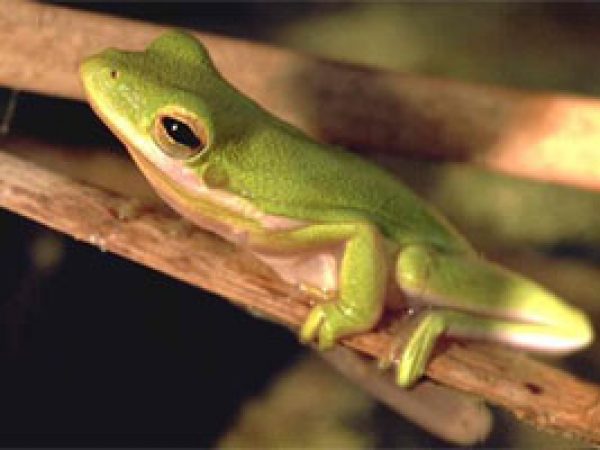
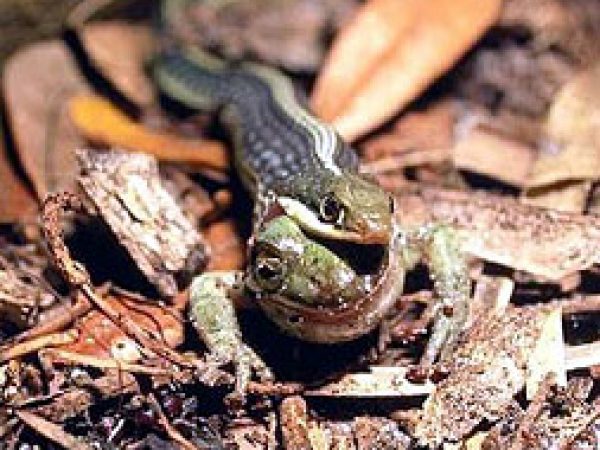
Rim Rock Crowned Snake (Tantilla oolitica). Photo © Kenneth Krysko Green treefrog (Hyla cinerea). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District
Green treefrog (Hyla cinerea). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District Brown Anole (Anolis sagrei). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey
Brown Anole (Anolis sagrei). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey Florida Ribbon Snake (Thamnophis sauritus sackenii). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District
Florida Ribbon Snake (Thamnophis sauritus sackenii). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District
Birds
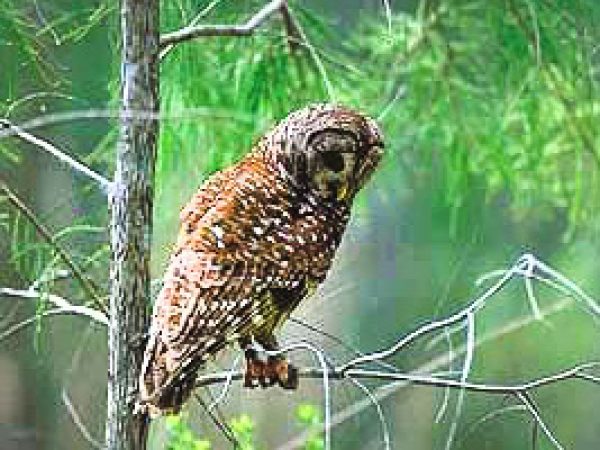
 Barred Owl (Strix varia). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District
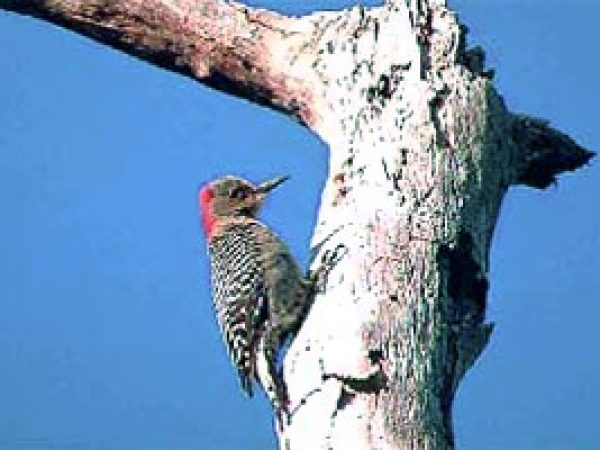
Barred Owl (Strix varia). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District Red-Bellied Woodpecker (Melanerpes carolinus). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District
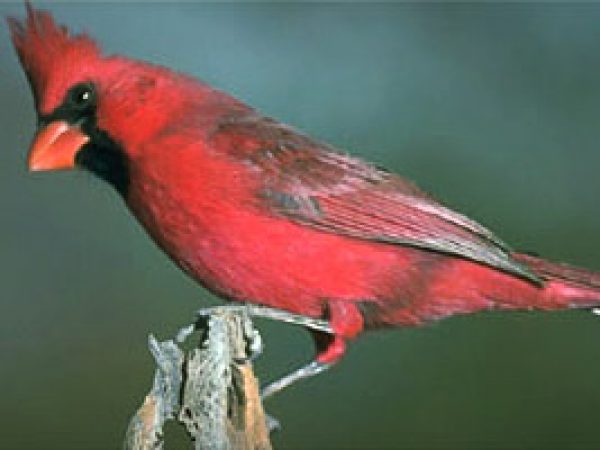
Red-Bellied Woodpecker (Melanerpes carolinus). Photo courtesy South Florida Water Management District Cardinal (Cardinalis cardinalis). Photo © Dr. Lloyd Glenn Ingles, California Academy of Sciences
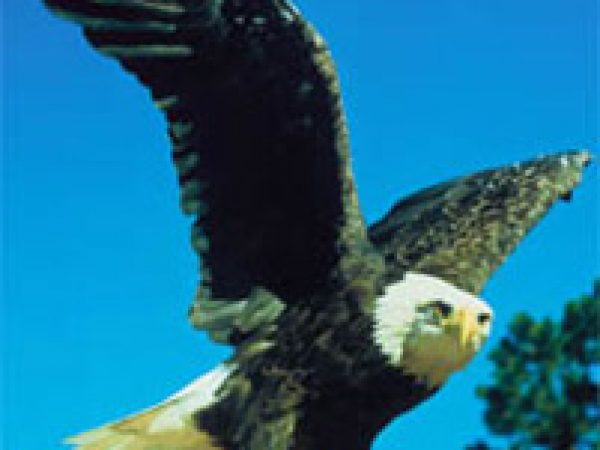
Cardinal (Cardinalis cardinalis). Photo © Dr. Lloyd Glenn Ingles, California Academy of Sciences Southern Bald Eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus leucocephalus). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
Southern Bald Eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus leucocephalus). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
Mammals
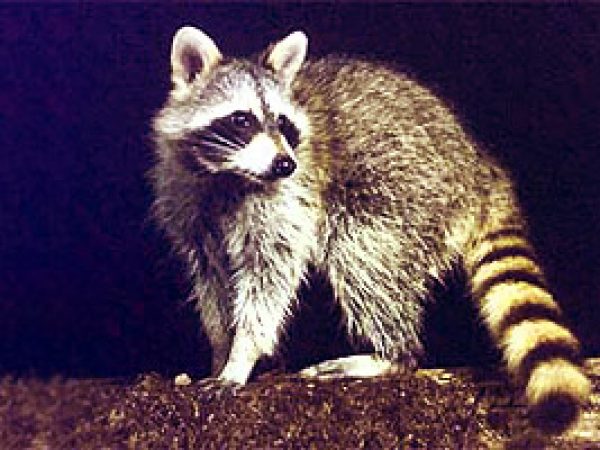
 Raccoon (Procyon lotor). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey
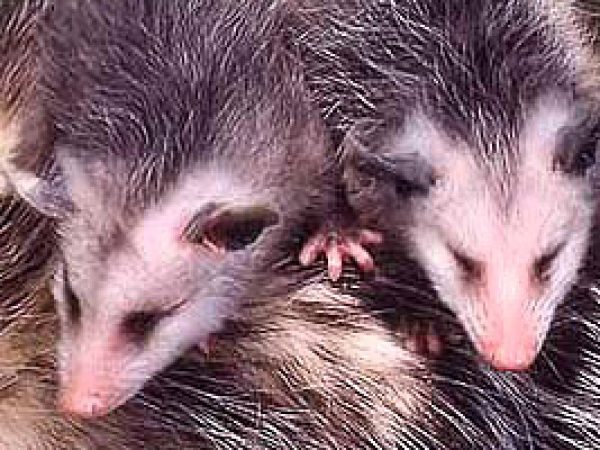
Raccoon (Procyon lotor). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey Opossum (Didelphis virginiana). Photo courtesy National Park Service
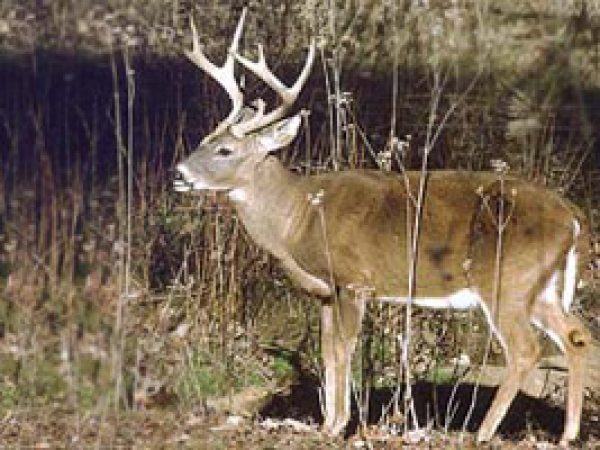
Opossum (Didelphis virginiana). Photo courtesy National Park Service White-tailed Deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey
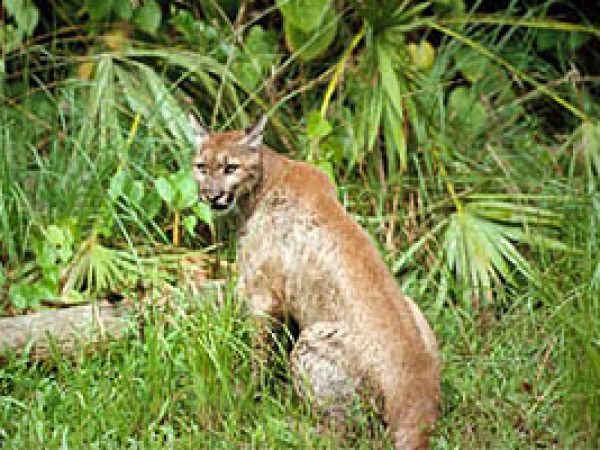
White-tailed Deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Photo courtesy U.S. Geological Survey Florida panther (Felis concolor coryi). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
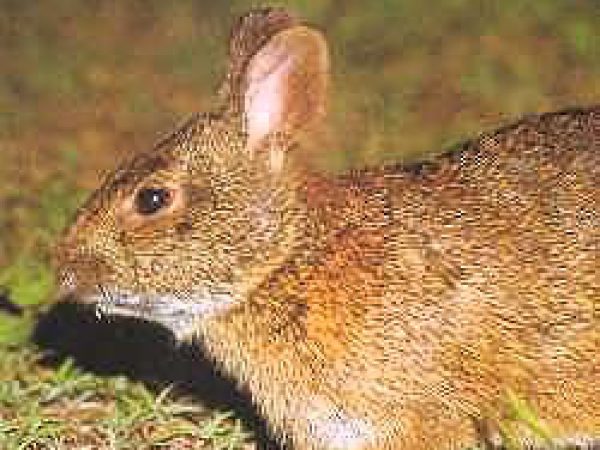
Florida panther (Felis concolor coryi). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Marsh Rabbit (Sylvilagus palustris). Photo courtesy National Park Service
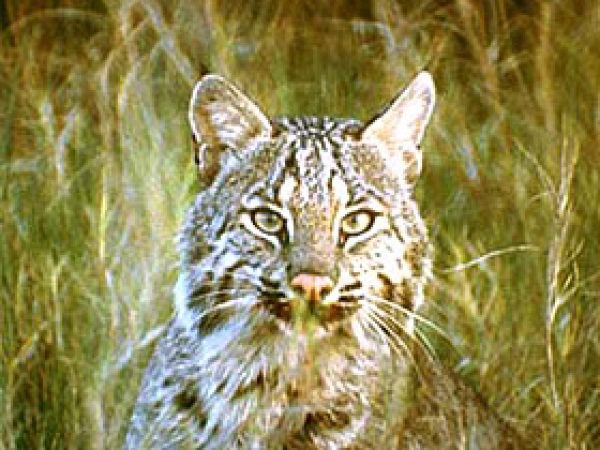
Marsh Rabbit (Sylvilagus palustris). Photo courtesy National Park Service Bobcat (Lynx rufus). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
Bobcat (Lynx rufus). Photo courtesy U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
- everglades mink (Mustela vison evergladensis), not shown
- cotton mouse (Peromyscus gossypinus), not shown
More rarely observed is the endangered Florida panther (Felis concolor coryi) as well as the Jamaica fruit bat (Artibeus jamaicensis) and Florida mastiff bat (Eumops glaucinus floridanus).
Glossary terms on page:
- hammock: area that is often higher than the surrounding land with humus rich soil and hardwood trees including oaks, sweetgums, hickories, and palms.
- canopy: uppermost layer of branches in a forest.
- temperate: temperate zone lies between 30 and 60 degrees latitude, climate undergoes seasonal changes in temperature and moisture.
- tropical: tropical zone lies between 23.5 degrees north and south of the equator, has small seasonal changes in temperature and large seasonal changes in precipitation.